C. Zhang, Y. Chen, K. Fan, G. Zhang, J. Zou, H. Dai, Y. Gao, X. Wang, M. Mao, C. Wang*, High-resolution mass spectroscopy for revealing the charge storage mechanism in batteries: Oxamide materials as an example. Energy Environ. Mater. 2022, DOI: 10.1002/EEM2.12557. (Invited article)
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/EEM2.12557
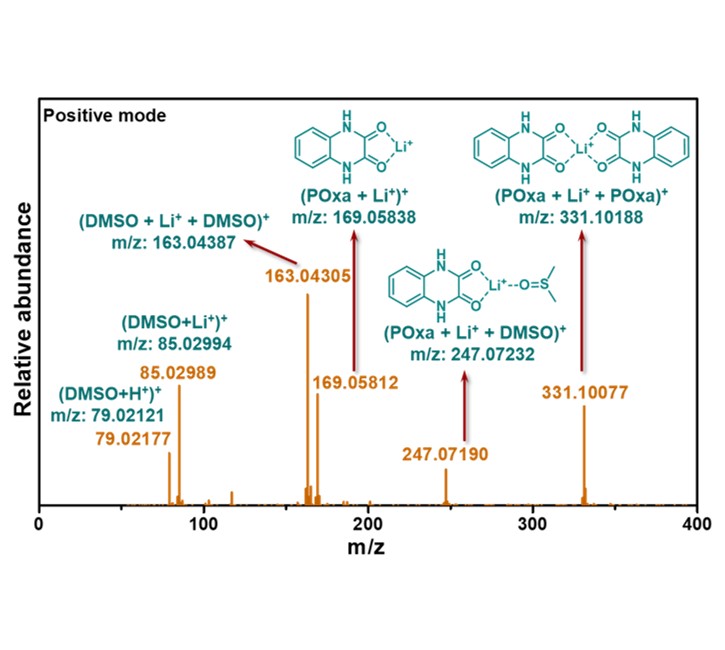
Abstract
The pursuit of high performance electrode materials is highly desired to meet the demand of batteries with high energy and power density. However, deep understanding of the charge storage mechanism is always challenging, which limits the development of advanced electrode materials. Herein, high-resolution mass spectroscopy (HR-MS) is employed to detect the evolution of organic electrode materials during the redox process and reveal the charge storage mechanism, by using small molecular oxamides as an example, which have ortho-carbonyls and are therefore potential electrochemical active materials for batteries. The HR-MS results adequately proved that the oxamides could reversibly store lithium ions in the voltage window of 1.5-3.8 V. Upon deeper reduction, the oxamides would decompose due to the cleavage of the C-N bonds in oxamide structures, which could be proved by the fragments detected by HR-MS, 1H NMR and the generation of NH3 after the reduction of oxamide by Li. This work provides a strategy to deeply understand the charge storage mechanism of organic electrode materials and will stimulate the further development of characterization techniques to reveal the charge storage mechanism for developing high performance electrode materials.
