G. Zhang#, L. Fu#, Y. Chen, K. Fan, C. Zhang, H. Dai, L. Guan, M. Mao, J. Ma*, C. Wang*, Hofmeister Effects in Supramolecular Chemistry for Anion-Modulation to Stabilize Zn Anode. Adv. Mater. 2024, DOI: 10.1002/adma.202405949.
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202405949
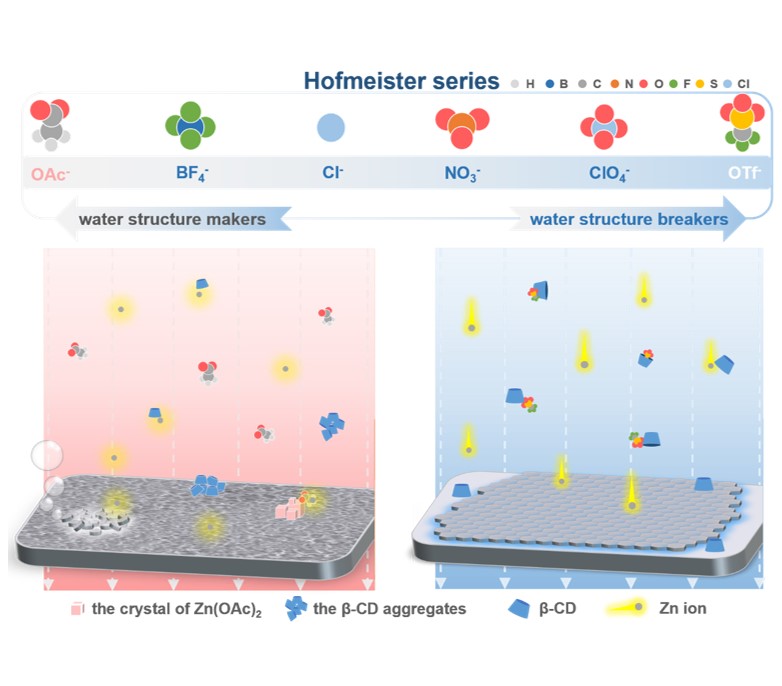
Abstract: Aqueous Zn-ion batteries (AZIBs) are considered as promising candidates for the next-generation large-scale energy storage, which, however, is facing the challenge of instable Zn anodes. The anion is pivotal in the stability of anodes, which have not been paid enough attention to. Herein, we report the modulation of anions using the Hofmeister series in supramolecular chemistry to boost the stability of Zn anodes. We found that the right-side anions in the Hofmeister series (e.g. OTf-) could enhance the Zn2+ transference number, increase the Coulombic efficiency, facilitate uniform Zn deposition, reduce the freezing point of electrolytes, and thereby stabilize the Zn anodes. More importantly, the right-side anions could form strong interaction with β-cyclodextrin compared to the left-side anions, and hence the addition of β-cyclodextrin could further enhance the stability of Zn anodes in OTf--based electrolytes, showing enhancement of cycling lifespan in the Zn//Zn symmetric cells more than 45.5 times with β-cyclodextrin compared with those without β-cyclodextrin. On the contrary, the left-side anions showed worse rate performance after the addition of β-cyclodextrin. These results provided an effective and novel approach to choose anions and matching additives to stabilize the anodes and achieve high-performance AZIBs through Hofmeister effect.
